Nurses need physiology collapsed lungs – Nurses play a vital role in recognizing and managing collapsed lungs, a serious condition that can lead to respiratory distress. This article delves into the physiology of collapsed lungs, nursing interventions, and the importance of collaboration with other healthcare professionals.
Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the lungs is essential for nurses to effectively assess and diagnose collapsed lungs. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, such as sudden onset of chest pain, shortness of breath, and decreased breath sounds, nurses can promptly initiate appropriate interventions.
Nurses’ Role in Recognizing Collapsed Lungs
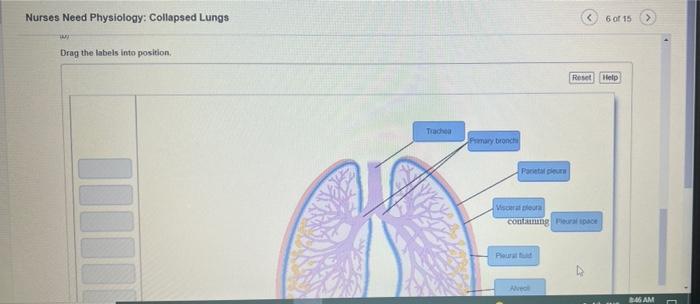
Nurses play a critical role in identifying and assessing collapsed lungs. They are often the first healthcare professionals to come into contact with patients experiencing respiratory distress, and they must be able to recognize the signs and symptoms of a collapsed lung in order to provide prompt and appropriate care.
Some of the signs and symptoms of a collapsed lung that nurses should be aware of include:
- Sudden onset of sharp, pleuritic chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid breathing
- Asymmetrical chest expansion
- Diminished breath sounds on the affected side
- Hyperresonance on percussion over the affected side
li>Cyanosis
Nurses use a variety of methods to diagnose collapsed lungs, including:
- Auscultation of the chest
- Percussion of the chest
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan
Physiology of Collapsed Lungs
The lungs are a pair of organs located in the chest cavity. They are responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the bloodstream and the air. The lungs are made up of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli.
When the alveoli collapse, they can no longer exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide, which can lead to a collapsed lung.
There are a number of different mechanisms that can lead to a collapsed lung, including:
- Trauma to the chest
- Spontaneous pneumothorax
- Tension pneumothorax
- Hydrothorax
- Hemothorax
The type of collapsed lung that occurs depends on the underlying cause.
Nursing Interventions for Collapsed Lungs
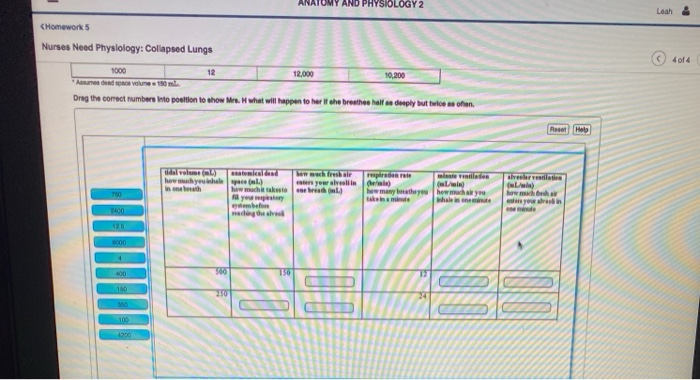
The nursing interventions used to manage collapsed lungs vary depending on the severity of the collapse. In some cases, simple measures such as rest and oxygen therapy may be sufficient. In other cases, more invasive interventions such as chest tube insertion or surgery may be necessary.
The rationale for each nursing intervention is to:
- Relieve pain
- Improve oxygenation
- Prevent further collapse
- Promote healing
Some examples of nursing care plans for patients with collapsed lungs include:
- Monitoring vital signs
- Administering oxygen therapy
- Inserting a chest tube
- Providing pain relief
- Educating the patient about collapsed lungs
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals
Nurses collaborate with a variety of other healthcare professionals in managing collapsed lungs. These professionals include:
- Physicians
- Respiratory therapists
- Radiologists
- Surgeons
Each of these professionals plays a specific role in the diagnosis and management of collapsed lungs. By working together, these professionals can provide the best possible care for patients.
Patient Education and Discharge Planning
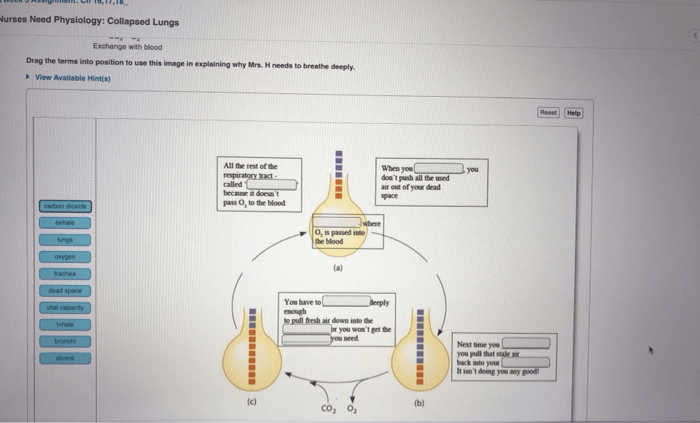
Nurses play a vital role in educating patients about collapsed lungs. This education includes information about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of collapsed lungs. Nurses also provide patients with instructions on how to care for themselves after they are discharged from the hospital.
Discharge planning is an important part of the nursing process. Nurses work with patients and their families to develop a plan for care after the patient is discharged from the hospital. This plan may include:
- Follow-up appointments
- Medications
- Activity restrictions
- Lifestyle changes
By providing patients with education and discharge planning, nurses can help them to manage their collapsed lungs and prevent future complications.
FAQ Overview: Nurses Need Physiology Collapsed Lungs
What are the common causes of collapsed lungs?
Collapsed lungs can result from various causes, including trauma, underlying lung disease, and certain medical procedures.
How do nurses diagnose collapsed lungs?
Nurses use a combination of physical examination, chest X-rays, and other diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of a collapsed lung.
What are the nursing interventions for collapsed lungs?
Nursing interventions include administering oxygen therapy, monitoring vital signs, providing chest physiotherapy, and assisting with pain management.