A sponsor proposes research to evaluate, opening a gateway to delve into the intricate process of assessing research proposals. This comprehensive guide navigates the multifaceted aspects of research proposal evaluation, exploring the motivations of sponsors, evaluation methods, data analysis, and decision-making.
Get ready to unravel the complexities of research proposal evaluation, empowering sponsors and researchers alike.
The second paragraph provides an overview of the significance of evaluating research proposals, highlighting the key factors to consider and examples of evaluation criteria. It sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the topic in subsequent sections.
1. Research Proposal Evaluation: A Sponsor Proposes Research To Evaluate
Evaluating research proposals is crucial to ensure the allocation of resources to high-quality research projects. It helps assess the potential impact, feasibility, and ethical considerations of the proposed research.
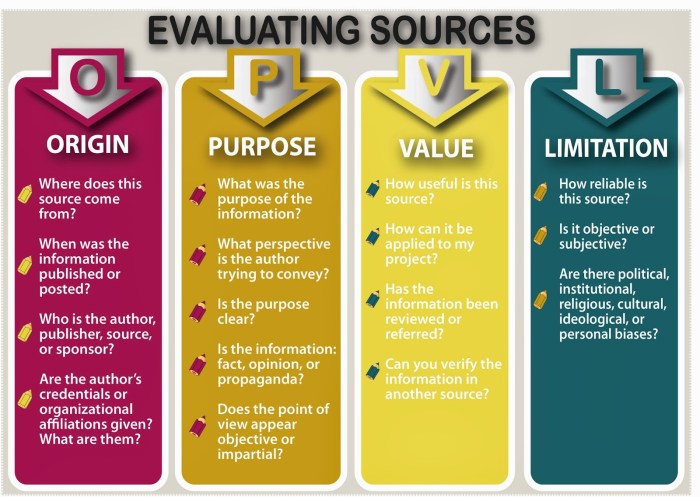
Key Factors to Consider
- Significance and originality of the research question
- Methodological rigor and feasibility
- Qualifications and experience of the research team
- Budget and resource allocation
- Ethical implications and data management plan
Evaluation Criteria
Specific evaluation criteria may vary depending on the research field and funding agency, but common criteria include:
- Scientific merit:Significance of the research question, originality, and potential impact
- Feasibility:Methodological rigor, resource availability, and research team’s expertise
- Qualifications:Experience and track record of the research team
- Budget:Appropriateness of the budget and resource allocation
- Ethics:Ethical implications, data management plan, and adherence to research regulations
2. Sponsor’s Perspective
Motivations for Proposing Research
- Advance scientific knowledge and innovation
- Address societal challenges or industry needs
- Enhance reputation and visibility
- Build relationships with research institutions
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- Access to cutting-edge research and innovation
- Positive impact on society or industry
- Enhanced reputation and credibility
Challenges:
- Financial investment and resource allocation
- Risk of research not meeting expectations
- Ethical and regulatory considerations
Expectations and Outcomes
Sponsors expect research proposals to:
- Address the funding agency’s priorities
- Be of high scientific merit and feasibility
- Have a clear plan for data management and dissemination
- Contribute to the sponsor’s mission and goals
3. Evaluation Methods

Peer Review
Peer review involves sending proposals to experts in the relevant field for evaluation. Strengths: Objectivity, expertise-based feedback. Limitations: Potential bias, workload on reviewers.
Expert Panels, A sponsor proposes research to evaluate
Expert panels consist of a group of experts who collectively evaluate proposals. Strengths: Comprehensive evaluation, diverse perspectives. Limitations: Time-consuming, potential for groupthink.
Scoring Systems
Scoring systems use predefined criteria to evaluate proposals based on a numerical scale. Strengths: Objective, quantifiable results. Limitations: Overemphasis on numerical scores, potential for bias.
Ethics and Transparency
Ethical considerations and transparency are crucial in the evaluation process. Evaluators must disclose potential conflicts of interest, and the evaluation process should be transparent and unbiased.
4. Data Analysis and Reporting

Data Table
| Evaluation Criteria | Score |
|---|---|
| Scientific Merit | 8/10 |
| Feasibility | 7/10 |
| Qualifications | 9/10 |
| Budget | 6/10 |
| Ethics | 8/10 |
Key Findings and Recommendations
The research proposal demonstrates strong scientific merit and a qualified research team. However, the budget allocation requires further justification, and the data management plan could be improved.
5. Decision-Making and Communication
Decision-Making Process
Funding decisions are made based on the evaluation results and the sponsor’s priorities. Sponsors may consider additional factors such as alignment with their mission and the potential impact of the research.
Communication of Funding Decisions
Sponsors communicate funding decisions to researchers in a timely and professional manner. They provide feedback on the evaluation results, both for funded and unfunded proposals.
Constructive Feedback for Unfunded Proposals
Sponsors provide constructive feedback to researchers whose proposals are not funded. This feedback can help researchers improve their future proposals and identify areas for improvement.
6. Best Practices and Future Directions

Best Practices
- Sponsors: Clearly define funding priorities and evaluation criteria.
- Researchers: Prepare high-quality proposals that address the funding agency’s requirements.
Future Directions
- Development of more standardized evaluation criteria and scoring systems.
- Use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to assist in the evaluation process.
- Continuous improvement and refinement of the evaluation process.
Importance of Continuous Improvement
Regular review and improvement of the evaluation process ensure its effectiveness, fairness, and alignment with the evolving research landscape.
FAQ Resource
What is the purpose of evaluating research proposals?
Evaluating research proposals ensures that the proposed research is scientifically sound, feasible, and aligns with the sponsor’s goals. It helps identify high-quality research that has the potential to make significant contributions to the field.
What are some key factors to consider when evaluating a research proposal?
Key factors include the research question, methodology, qualifications of the исследователь, budget, and potential impact. Evaluators assess each proposal based on its strengths and weaknesses in these areas.
What are some common evaluation methods used for research proposals?
Common evaluation methods include peer review, expert panels, and scoring systems. Peer review involves soliciting feedback from experts in the field, while expert panels provide a more structured evaluation process. Scoring systems assign numerical values to different aspects of the proposal, allowing for a more quantitative assessment.