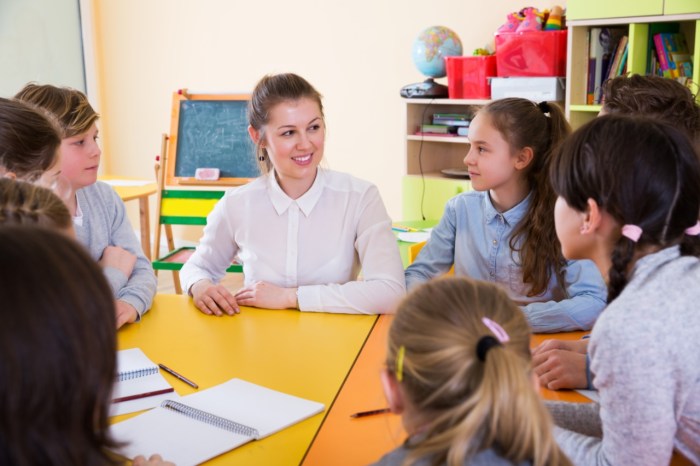
Entrance into formal schooling is considered important because it marks a significant transition in a child’s life, fostering their development in various aspects. From cognitive abilities to social skills, formal schooling plays a pivotal role in shaping a child’s future success.
As children embark on their educational journey, they are exposed to a structured environment that promotes their cognitive growth. Through problem-solving exercises, critical thinking challenges, and opportunities for creativity, formal schooling nurtures children’s intellectual curiosity and lays the foundation for lifelong learning.
Entrance into Formal Schooling: Importance for Child Development
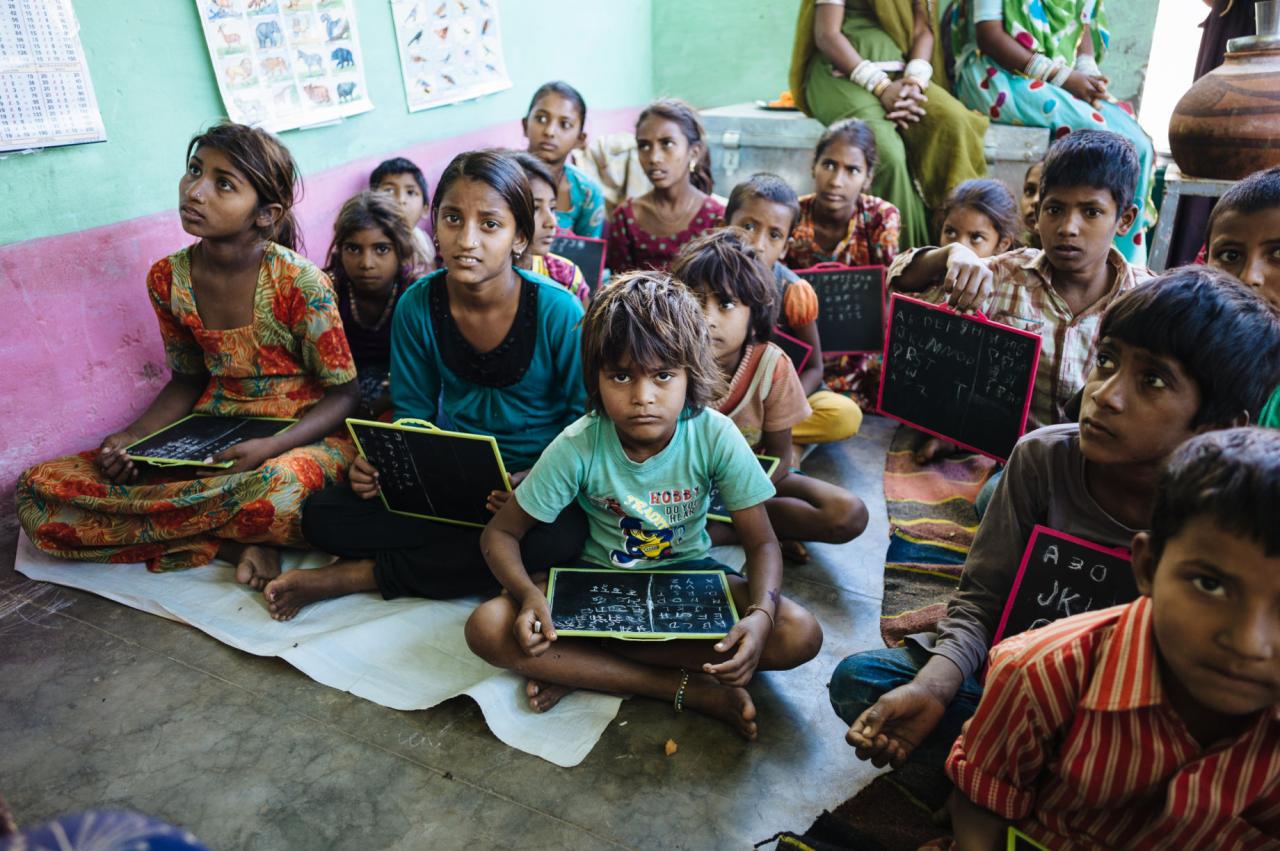

Formal schooling is considered important because it marks the beginning of a child’s formal education and is widely recognized as a crucial stage in their overall development. It provides children with the opportunity to acquire knowledge, skills, and experiences that are essential for their future success.
Formal schooling contributes to children’s social, emotional, cognitive, language and literacy, physical, cultural, and moral development.
Social and Emotional Development

Formal schooling plays a vital role in children’s social and emotional growth. It provides a structured environment where children interact with peers and adults outside their family, helping them develop social skills such as cooperation, communication, and empathy. Through group activities and projects, children learn to work together, resolve conflicts peacefully, and respect different perspectives.
School also provides opportunities for children to develop their emotional intelligence by learning to identify and manage their emotions, build self-esteem, and cope with challenges.
Cognitive Development
Formal schooling contributes significantly to children’s cognitive development. It provides a systematic and sequential curriculum that helps children develop their problem-solving skills, critical thinking abilities, and creativity. Through hands-on activities, experiments, and discussions, children learn to analyze information, draw inferences, and generate original ideas.
School also fosters children’s curiosity and encourages them to become lifelong learners by exposing them to a wide range of subjects and perspectives.
Language and Literacy Development
Formal schooling plays a critical role in children’s language and literacy development. It provides a structured environment where children are exposed to a rich vocabulary, grammar, and syntax. Through reading, writing, and speaking activities, children develop their comprehension, fluency, and vocabulary.
School also helps children develop a love of reading and writing by introducing them to different genres, authors, and writing styles.
Physical Development, Entrance into formal schooling is considered important because it marks
While not the primary focus, formal schooling can contribute to children’s physical development. It provides opportunities for physical activity through recess, physical education classes, and extracurricular activities. These activities help children develop their gross motor skills, fine motor skills, and coordination.
Physical activity is essential for children’s overall health and well-being, and school can play a role in promoting healthy habits.
Cultural and Moral Development
Formal schooling contributes to children’s cultural and moral development. It provides a context for children to learn about different cultures, traditions, and perspectives. Through history, geography, and social studies classes, children develop an understanding of their own cultural identity and a respect for others.
School also helps children develop a sense of right and wrong and make responsible decisions by teaching them about ethics, values, and citizenship.
Quick FAQs: Entrance Into Formal Schooling Is Considered Important Because It Marks
Why is formal schooling considered important for children’s social development?
Formal schooling provides children with opportunities to interact with peers and adults from diverse backgrounds, fostering their social skills, such as cooperation, communication, and empathy.
How does formal schooling contribute to children’s cognitive development?
Formal schooling exposes children to a wide range of subjects and learning experiences, stimulating their critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and creativity.
What role does formal schooling play in children’s language and literacy development?
Formal schooling provides systematic instruction in language and literacy skills, helping children develop their vocabulary, reading comprehension, and writing abilities.