Topic 2 proportionality skills practice – Topic 2: Proportionality Skills Practice embarks on an educational journey that delves into the intricacies of proportionality, empowering learners with the ability to solve complex problems and make informed predictions in various fields.
This module provides a comprehensive understanding of proportionality, including its concept, types, and applications. It equips students with step-by-step problem-solving strategies and demonstrates the practical uses of proportionality in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Proportionality
Proportionality refers to the relationship between two quantities where one quantity changes in direct proportion to the other. In other words, as one quantity increases, the other quantity also increases or decreases by a constant factor.
Types of Proportionality
- Direct Proportionality:The ratio of the two quantities remains constant as they change. For example, the distance traveled by a car is directly proportional to the time taken, assuming constant speed.
- Inverse Proportionality:The ratio of the two quantities varies inversely as they change. For example, the time taken to complete a task is inversely proportional to the number of people working on it, assuming constant efficiency.
- Joint Proportionality:The relationship between two or more quantities where the value of one quantity is proportional to the product or quotient of the other quantities. For example, the volume of a rectangular prism is jointly proportional to its length, width, and height.
Solving Proportionality Problems: Topic 2 Proportionality Skills Practice

Steps for Solving Proportionality Problems
- Identify the two quantities that are proportional.
- Set up a proportion equation using the two quantities and the constant of proportionality.
- Cross-multiply to solve for the unknown quantity.
Cross-Multiplication
Cross-multiplication is a method used to solve proportionality problems by multiplying the numerator of one fraction by the denominator of the other fraction and vice versa.
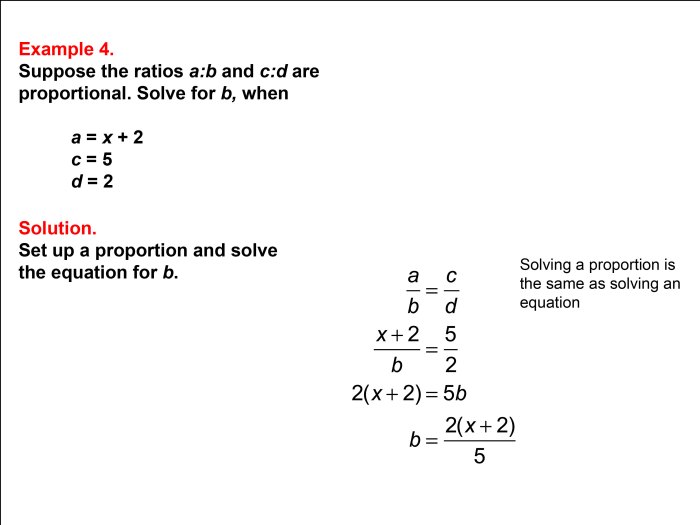
For example, to solve the proportion a/b = c/dfor a, we cross-multiply as follows:
a- d = b – c
Applications of Proportionality
Fields where Proportionality is Used
- Physics (e.g., Boyle’s Law, Ohm’s Law)
- Chemistry (e.g., stoichiometry, dilutions)
- Biology (e.g., allometric scaling, population growth)
- Engineering (e.g., structural design, fluid mechanics)
- Economics (e.g., supply and demand, elasticity)
Examples of Proportionality in Real-World Situations, Topic 2 proportionality skills practice
- The cost of groceries is proportional to the quantity purchased.
- The distance traveled by a car is proportional to the speed at which it travels.
- The time it takes to fill a pool is inversely proportional to the number of hoses used.
Practice Exercises
| Exercise | Difficulty | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| Find the value of x in the proportion 3/5 = x/10. | Easy | 6 |
| The speed of a train is inversely proportional to the time it takes to travel a certain distance. If the train travels 120 miles in 2 hours, how long will it take to travel 240 miles? | Medium | 4 hours |
| The volume of a rectangular prism is jointly proportional to its length, width, and height. If a prism with length 5 cm, width 3 cm, and height 2 cm has a volume of 30 cm³, what is the volume of a prism with length 10 cm, width 6 cm, and height 4 cm? | Hard | 120 cm³ |
FAQ Overview
What is the concept of proportionality?
Proportionality refers to a relationship between two or more variables where a change in one variable causes a proportional change in the other(s).
How do you solve proportionality problems?
Solving proportionality problems involves setting up and solving equations based on the principle that the ratio of one variable to another remains constant.
What are the different types of proportionality?
There are two main types of proportionality: direct proportionality (where variables change in the same direction) and inverse proportionality (where variables change in opposite directions).
