Staph bacteria are responsible for milady, causing a wide range of infections that can be both mild and life-threatening. Understanding the characteristics, pathogenicity, and transmission of staph bacteria is crucial for effective diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Staphylococcus bacteria, commonly known as staph, are Gram-positive, spherical bacteria that can form clusters or chains. They possess a thick cell wall containing virulence factors that contribute to their pathogenicity. Staph bacteria are responsible for a diverse array of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, pneumonia, and sepsis.
Staph Bacteria Characteristics: Staph Bacteria Are Responsible For Milady
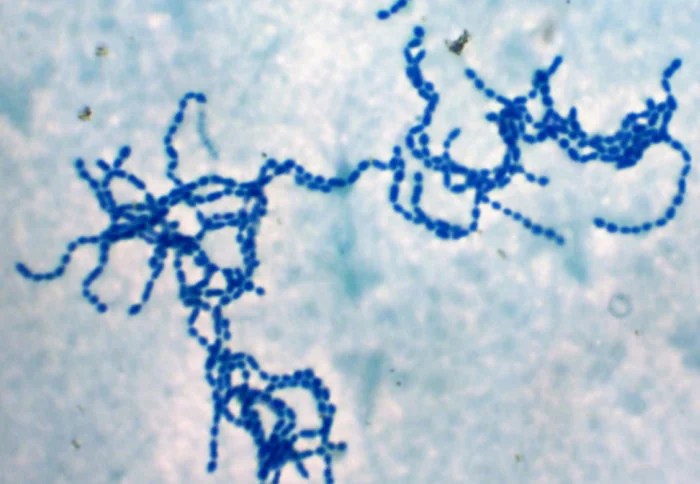
Staphylococci are Gram-positive, spherical bacteria that are commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and other animals. They are facultative anaerobes, meaning they can grow in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. Staphylococci are classified into two main species: Staphylococcus aureusand Staphylococcus epidermidis. S. aureusis the most common cause of staph infections in humans, while S. epidermidisis typically associated with infections in immunocompromised individuals.
Staphylococci have a thick cell wall that contains peptidoglycan and teichoic acid. The cell wall is responsible for the Gram-positive staining properties of staphylococci. Staphylococci also produce a variety of virulence factors, including toxins, enzymes, and adhesins. These virulence factors enable staphylococci to adhere to host cells, invade tissues, and evade the immune system.
Morphology and Structure, Staph bacteria are responsible for milady
Staphylococci are typically arranged in grape-like clusters. This is due to the fact that they divide in multiple planes, resulting in the formation of irregular clumps of cells. Staphylococci are non-motile and do not form spores.
Pathogenicity of Staph Bacteria
Staphylococci are responsible for a wide range of infections in humans, including skin infections, pneumonia, and sepsis. Skin infections are the most common type of staph infection. They can range from minor skin rashes to serious infections, such as cellulitis and abscesses.
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by staphylococci. It is a serious infection that can lead to hospitalization and even death. Sepsis is a life-threatening infection that can occur when bacteria enter the bloodstream. Staphylococci are a common cause of sepsis, and it is a major cause of death in hospitals.
Staphylococci produce a variety of virulence factors that enable them to cause disease. These virulence factors include toxins, enzymes, and adhesins. Toxins are proteins that can damage host cells and tissues. Enzymes can help staphylococci to invade host cells and tissues.
Adhesins are proteins that help staphylococci to adhere to host cells.
Transmission and Epidemiology
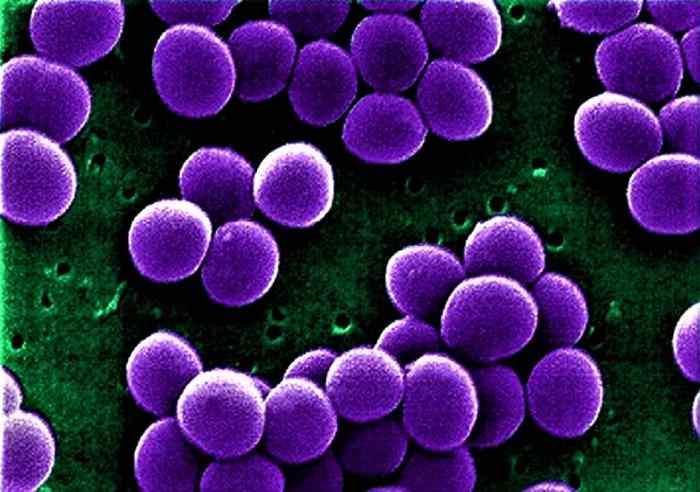
Staphylococci are transmitted through contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces. Staphylococci can be found on the skin and mucous membranes of healthy individuals, and they can be spread through direct contact with these individuals. Staphylococci can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as doorknobs, countertops, and medical equipment.
Staph infections are a major public health problem. In the United States, staph infections are the most common cause of skin and soft tissue infections. Staph infections are also a leading cause of pneumonia and sepsis. The incidence of staph infections has been increasing in recent years, and this is due in part to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of staphylococci.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Staph infections are diagnosed based on the patient’s symptoms and a physical examination. A doctor may also order laboratory tests, such as a culture and sensitivity test, to confirm the diagnosis. A culture and sensitivity test can identify the specific type of bacteria that is causing the infection and determine which antibiotics are effective against it.
Staph infections are treated with antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic will depend on the type of staph infection and the patient’s overall health. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to drain an abscess or remove infected tissue.
Prevention and Control
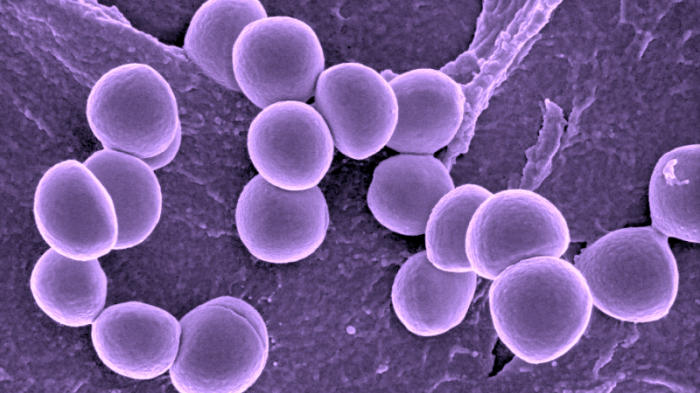
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent staph infections. These include:
- Washing your hands frequently with soap and water.
- Covering any open wounds with a bandage.
- Avoiding contact with people who are sick.
- Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that are frequently touched.
- Getting vaccinated against staph infections.
Antimicrobial stewardship is also important for preventing the spread of staph infections. Antimicrobial stewardship is a set of practices that are designed to ensure that antibiotics are used appropriately. This includes using the right antibiotic for the right infection, using the right dose of antibiotic, and using antibiotics for the right amount of time.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the common symptoms of staph infections?
Symptoms of staph infections vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include skin redness, swelling, pain, and drainage of pus.
How are staph infections treated?
Staph infections are typically treated with antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type and severity of the infection.
How can staph infections be prevented?
Staph infections can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, such as handwashing, covering wounds, and avoiding contact with infected individuals or surfaces.