Frame scaffolds which exceed 4 times – Frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height present unique safety hazards and engineering challenges. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate measures is crucial for ensuring worker safety and project success.
The implications of using frame scaffolds beyond their designed capacity extend beyond potential accidents. These structures require specialized design considerations, rigorous inspection and maintenance procedures, and comprehensive training and supervision to mitigate risks.
Frame Scaffolds Exceeding 4 Times
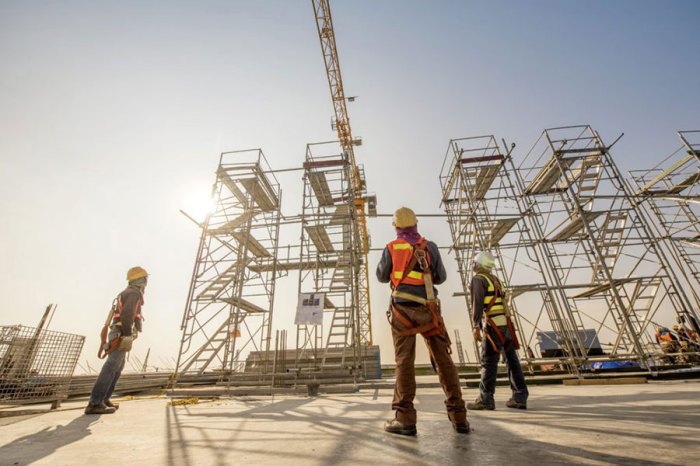

Frame scaffolds are temporary structures used to provide access to elevated work areas. They are typically made of metal or wood and consist of a series of frames that are connected together. The allowable height of a frame scaffold is typically 4 times the base width.
Using frame scaffolds that exceed 4 times their allowable height can be dangerous. The scaffold may become unstable and collapse, causing injury or death to workers. Additionally, the scaffold may not be able to support the weight of the workers and materials, which can also lead to collapse.
Examples of Situations Where Frame Scaffolds Exceeding 4 Times Are Used
- When there is no other way to reach the work area.
- When the work area is very high.
- When the work area is very large.
Safety Considerations
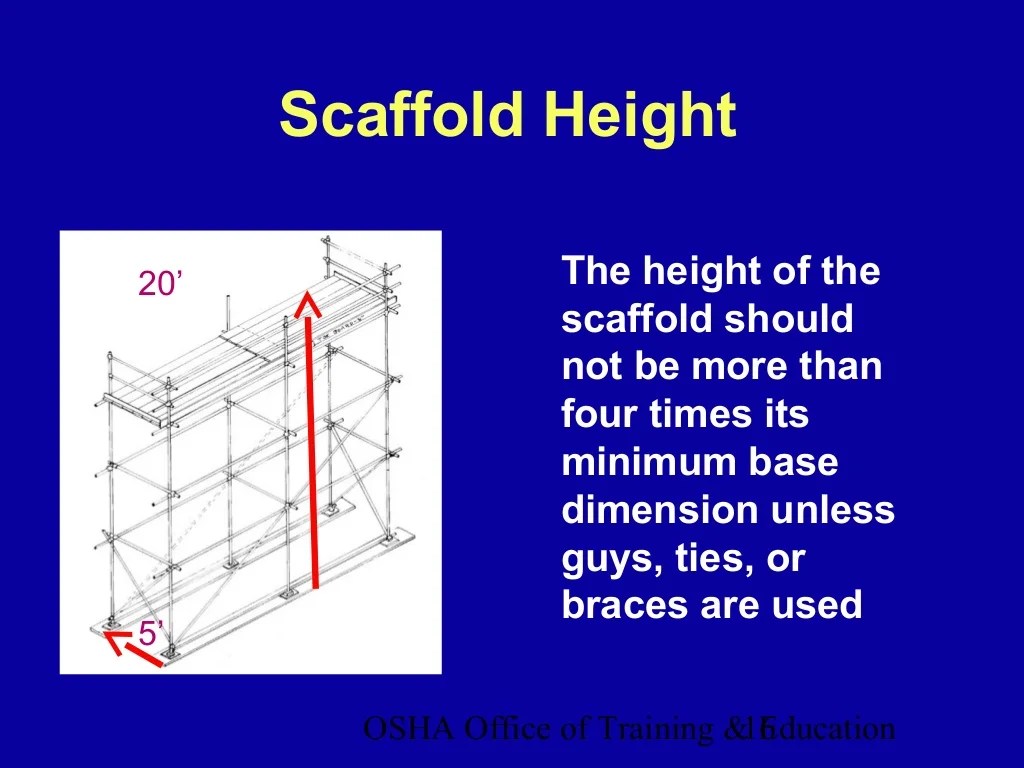
Frame scaffolds exceeding 4 times their allowable height pose significant safety hazards due to increased instability and potential for collapse. These hazards include:
- Excessive Sway:Tall scaffolds are more susceptible to swaying, especially in high winds or under heavy loads.
- Buckling:Excessive height can lead to buckling of the scaffold’s components, resulting in a catastrophic collapse.
- Tip-over:Tall scaffolds have a higher center of gravity, making them more likely to tip over if not properly secured.
To ensure the safety of workers using these scaffolds, the following measures should be taken:
- Rigorous Inspection:Scaffolds must be thoroughly inspected before each use and after any modifications or adverse weather conditions.
- Secure Base:The scaffold must be erected on a stable and level surface and securely anchored to prevent movement.
- Adequate Bracing:Additional bracing should be used to increase the stability of tall scaffolds.
- Height Restriction:The scaffold should not exceed the allowable height limit, as determined by the manufacturer or relevant safety regulations.
Safety Regulations and Standards
The following table Artikels key safety regulations and standards related to frame scaffolds:
| Regulation/Standard | Requirement |
|---|---|
| OSHA 29 CFR 1926.451(g)(1) | Scaffolds exceeding 4 times their height are prohibited. |
| ANSI A10.8-2017 | Provides guidelines for the design, construction, and use of frame scaffolds, including height restrictions. |
| SIA 299:2015 | European standard that addresses the safety requirements for frame scaffolds, including height limits. |
Engineering Design
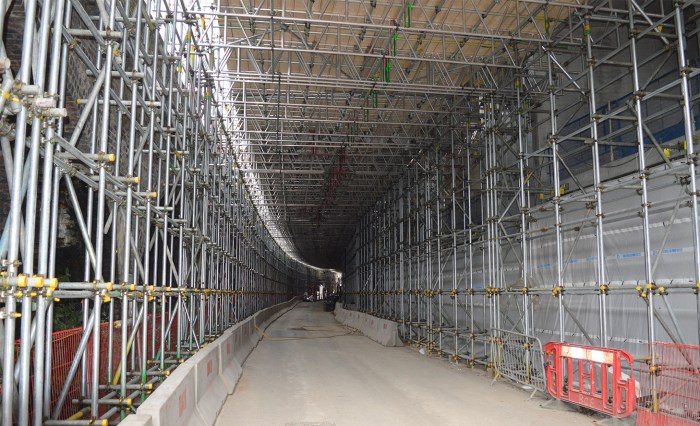

Engineering considerations for designing frame scaffolds that exceed 4 times their allowable height are critical to ensure structural stability and safety. These scaffolds must be designed to withstand increased loads and lateral forces while maintaining adequate stability.
Materials and Methods
Frame scaffolds exceeding 4 times their allowable height typically utilize high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum. The scaffold components, including frames, braces, and platforms, are designed with increased thickness and strength to handle the additional loads. Additionally, these scaffolds often employ advanced engineering techniques like moment-resisting connections and bracing systems to enhance stability.
Structural Design
The structural design of frame scaffolds exceeding 4 times their allowable height involves careful analysis of load distribution and stress concentrations. Engineers use computer modeling and testing to optimize the scaffold’s geometry and component sizes to ensure adequate strength and stability.
The scaffolds are designed to resist wind loads, seismic forces, and other environmental factors.
The structural design also includes provisions for safe access and egress, such as integrated ladders and guardrails. These features ensure that workers can safely navigate the scaffold while performing their tasks.
Illustrations
The following illustrations demonstrate the structural design of frame scaffolds exceeding 4 times their allowable height:
- Diagram of a braced frame scaffold with moment-resisting connections
- Computer model showing load distribution and stress concentrations in a scaffold
Inspection and Maintenance

Frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height require rigorous inspection and maintenance procedures to ensure their safety and stability. Regular inspections help identify potential hazards, such as loose connections, damaged components, or excessive corrosion, allowing for timely repairs and preventing accidents.
Inspection Requirements, Frame scaffolds which exceed 4 times
- Daily Inspections:Conducted by the scaffold erector or a competent person before each shift and after any significant event, such as storms or earthquakes.
- Weekly Inspections:Performed by a qualified inspector to assess the overall condition of the scaffold, including its structural integrity, connections, and any attachments.
- Monthly Inspections:Conducted by a registered professional engineer to evaluate the scaffold’s stability, load-bearing capacity, and compliance with design specifications.
Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is essential to maintain the integrity of the scaffold. This includes:
- Tightening Loose Connections:Regularly check and tighten all bolts, nuts, and other connections to ensure the scaffold remains stable.
- Replacing Damaged Components:Promptly replace any damaged or corroded components, such as planks, braces, or uprights, to prevent failure.
- Lubricating Moving Parts:Lubricate all moving parts, such as pulleys and winches, to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature wear.
- Cleaning and Painting:Regularly clean and paint the scaffold to protect it from corrosion and enhance its visibility.
By adhering to these inspection and maintenance procedures, the safety and reliability of frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height can be ensured, minimizing the risk of accidents and protecting the well-being of workers.
Training and Supervision

Workers using frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height require specialized training and supervision to ensure safety and prevent accidents. This section discusses the training and supervision requirements, the responsibilities of supervisors and workers, and Artikels the necessary training and supervision elements.
Training programs for workers using frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height should include both theoretical and practical components. Theoretical training should cover topics such as scaffold design, inspection, and maintenance, as well as the hazards associated with working at elevated heights.
Practical training should provide hands-on experience in erecting, dismantling, and inspecting frame scaffolds.
Responsibilities of Supervisors
Supervisors are responsible for ensuring that workers are properly trained and supervised when using frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height. They should also ensure that the scaffolds are erected, inspected, and maintained in accordance with applicable safety regulations.
- Develop and implement a training program for workers.
- Supervise workers during scaffold erection, dismantling, and inspection.
- Ensure that scaffolds are erected, inspected, and maintained in accordance with applicable safety regulations.
- Take appropriate disciplinary action against workers who violate safety regulations.
Responsibilities of Workers
Workers are responsible for following the safety regulations and procedures when using frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height. They should also report any unsafe conditions to their supervisor.
- Follow the safety regulations and procedures when using frame scaffolds.
- Report any unsafe conditions to their supervisor.
- Use proper personal protective equipment (PPE) when working on scaffolds.
- Participate in training programs and follow the instructions of their supervisor.
Case Studies

Numerous incidents involving frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height have been documented, leading to severe consequences. Analyzing these case studies can provide valuable insights into the causes of such incidents and guide the development of effective prevention strategies.
One notable case study involved a scaffold collapse in 2017, resulting in multiple fatalities and injuries. The investigation revealed that the scaffold exceeded its allowable height by a significant margin, and the base was not adequately secured, leading to instability and collapse.
Common Causes of Incidents
- Exceeding the allowable height of the scaffold.
- Inadequate base securing, resulting in instability.
- Lack of proper bracing and support systems.
- Overloading the scaffold with excessive weight.
- Failure to conduct regular inspections and maintenance.
These case studies highlight the critical importance of adhering to safety guidelines and industry standards when working with frame scaffolds. By implementing best practices, such as regular inspections, proper assembly, and adequate bracing, similar incidents can be prevented.
Expert Answers: Frame Scaffolds Which Exceed 4 Times
What are the primary safety hazards associated with frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height?
These scaffolds are more susceptible to instability, wind loads, and overloading, increasing the risk of collapse and falls.
What engineering considerations are crucial for designing frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height?
Material strength, structural integrity, and stability must be carefully calculated to withstand the increased loads and stresses.
Why are regular inspections and maintenance essential for frame scaffolds exceeding four times their allowable height?
Regular inspections identify potential defects, corrosion, or damage that could compromise the scaffold’s safety and stability.